

Dr. Tariq Jagnarine
Fam Med, Endocrinology / Diabetes
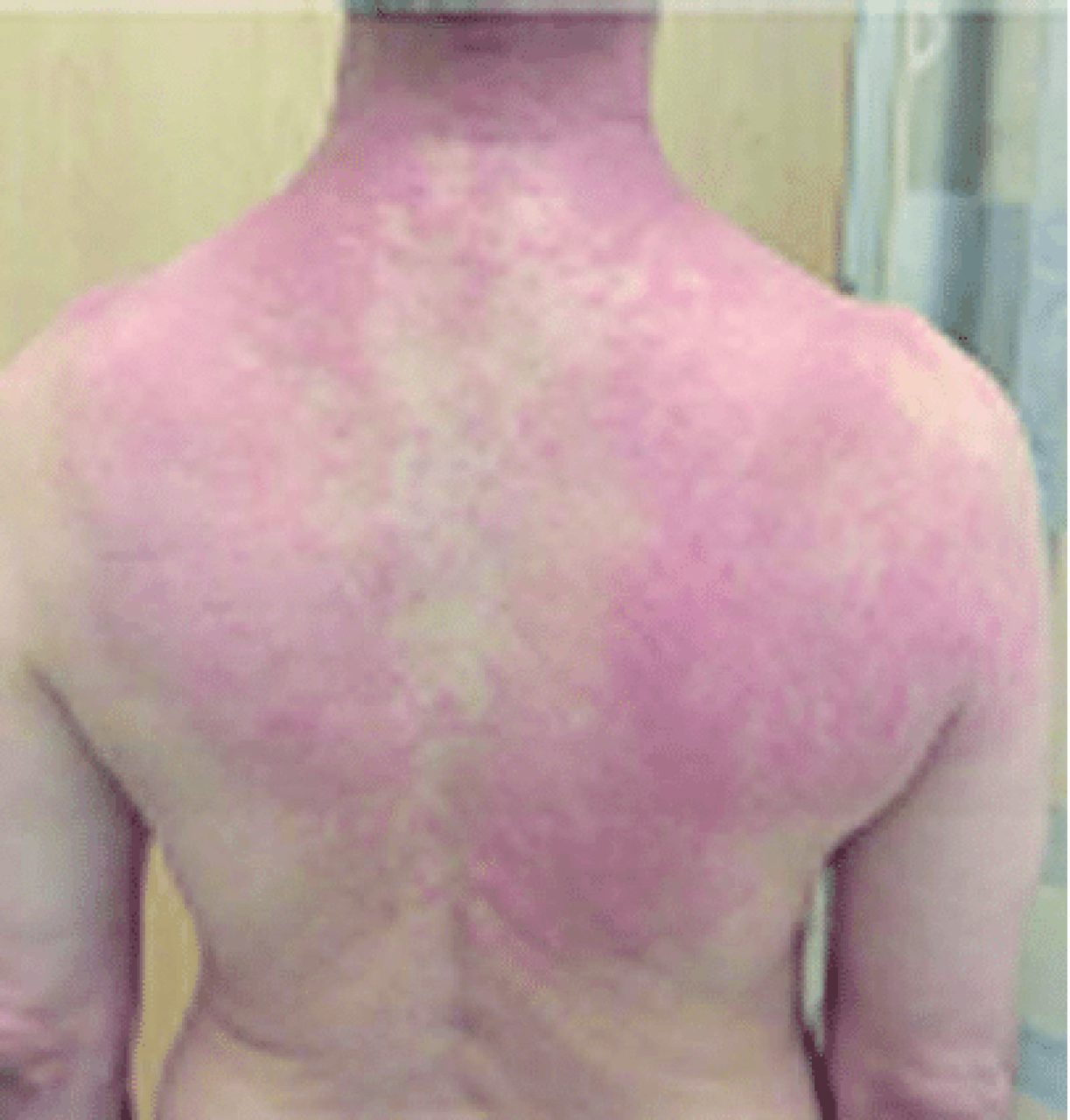
Most people experience the unpleasant itching of contact dermatitis at least once in their lifetime. Although most people do not experience a major allergic reaction, the effects of contact dermatitis can be undesirable until they subside. When an individual’s skin comes into contact with an irritating substance, they can develop a itching or burning rash. This reaction is called contact dermatitis.
TYPES OF CONTACT DERMATITIS
Although contact dermatitis may seem to develop out of nowhere, there are several common types:
Inflammatory contact dermatitis is the most common form of contact dermatitis. It occurs when the skin touches an irritating chemical, experiences excessive friction, or contacts heat.
* Allergic contact dermatitis is caused by an allergic reaction or by the immune system over-reacting to a substance or chemical.
Contact urticaria, also known as hives, is a less common form of allergic contact dermatitis that occurs immediately after exposure to an allergen.
* Occupational contact dermatitis occurs in some professions where workers may have frequent exposure to irritants or allergens, such as rubber, latex, or chemicals. These people include healthcare workers, hairdressers, and food servers among many others.
* Photocontact dermatitis occurs after a person comes into contact with an irritant or allergen after which the contact area is exposed to the sun causing a reaction.
In all of these cases, an itching or burning rash appears either immediately or within a few days. It is important that people treat the rash and know what triggered it to avoid future contact dermatitis.
RISK FACTORS FOR CONTACT DERMATITIS
* Age: More common with age
* Gender: females
Atopic dermatitis
* Genetic factor
CONTACT DERMATITIS SYMPTOMS
In almost all cases of contact dermatitis, a rash develops after exposure to an allergen or irritant. In most cases of contact dermatitis, the rash will be red, itchy, and may sting. If exposure to irritant or allergen persists, the skin may become dark and leathery.
In addition, some types of contact dermatitis have the following symptoms:
* Blisters
* Dry, cracked, and flaky skin
* Measles rash
* Burn sensation
* Pain or itching
* Swelling
To distinguish types of contact dermatitis, a person should pay attention to it when the symptoms start.
When contact dermatitis develops due to an inflammatory reaction, symptoms may occur immediately after contact with the irritant. Ulcers can also develop in severe cases, which allows the individual to recognize the triggering irritation.
In cases of photocontact dermatitis, the rash appears only after exposure to sunlight.
COMMON DRIVERS
The triggers vary from person to person and by type of contact dermatitis. It is important to know what triggers a reaction to avoid future exposure to the substance. The following are some of the most common triggers for the different types of contact dermatitis.
Allergic reaction triggers include:
*
* Rubber
Poison ivy, poison oak, and poison sumac
* Medicines applied to the skin
* Fragrances in soap
* Tanning agent found in leather products
* Skin cream
* Deodorant
* Shaving cream
* Latex
* Nickel or gold jewelery
* Citrus fruits
* Cosmetics
Perfume
Hair colour
In most cases, allergic reactions do not occur at the first contact with the substance. At first contact, the person tends to have a sensitivity to the irritant. It is only with a second exposure that the person develops a rash or other symptoms.
Inflammatory response triggers include:
Pepper spray
* Bleach
Hand sanitizer
* Battery acid
* Detergent
* Kerosene
* Drainage and other cleaners
Inflammatory reactions are not limited to toxic or more corrosive substances. In some cases, exposure to the same substance often causes reactions. For example, people who frequently wash their hands may develop an inflammatory response to the soap they use.
Photocontact reaction triggers can include:
* Shaving cream
* Skin cream
* Specific oils
* Specific remedies
Photocontact reactions occur less frequently than allergic or inflammatory reactions. For the reaction to occur, a person first needs to be exposed to the substance and then to the sun. An individual who uses cream before bed may never know that it is photosensitive to the product because it is absorbed long before exposure to the sun.
TREATMENT
In most cases, the rash and other reactions will disappear once exposure to the substance is over. The rash may take some time to heal and go away fully. For example, a rash of poison ivy often lies because the plant’s oils have flooded into the skin. Once the oil has disappeared, the rash clears.
It is best for a person to avoid exposure to substances that have been identified as causing contact dermatitis.
If connected, it’s a good idea to clean the area with some soap and mild water to prevent a rash developing. Most treatment options include home remedies. They include:
* Apply anti-itching cream to infected skin – steroid creams
* Oatmeal bath (or similar)
* Anti-histamine drugs
* Avoid scraping the infected area to help prevent infections
In extreme cases, a person may need to see a dermatologist, allergist, or other healthcare professional. They can prescribe creams, creams, or prescription drugs to treat contact dermatitis.
PREVENTION
In most cases, prevention is as simple as avoiding the substance or object that caused the contact dermatitis in the first place. For example, someone who develops a rash after coming into contact with poison ivy should try to avoid the plant. However, a person may not know what caused the reaction. If the exact cause is not known, someone may want to record things they come into contact with to help determine what might be causing the reaction. Often, a person may not consider that a change in skin care products could be the source of itching.
An allergist may be able to identify the allergen or irritant from a list of substances that the person came into contact with over the previous 24 to 48 hours. In other cases, the allergist may use skin tests to help determine the cause of a reaction.
If people start to experience the above symptoms along with swelling of the eyelids, tongue, shortness of breath – contact a healthcare provider immediately.
Have a lovely Easter and stay safe from allergens.
